Archives
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-11
- 2018-10
- 2018-07
-
Several cases of injury to the
2019-04-30
Several cases of injury to the circumflex artery owing to ablation of the lateral mitral isthmus and inside the CS have been reported. The circumflex artery and the CS share a close relationship. Takahashi et al. reported the first case of acute circumflex artery occlusion during CS ablation, which
-
br Drug resistant tuberculosis threatens to undermine
2019-04-30
Drug-resistant tuberculosis threatens to undermine advances in tuberculosis control worldwide. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDRTB), defined as resistance to isoniazid and rifampicin, requires treatment for up to 24 months with expensive diagnostics and second-line drugs. Fewer than 15% of pat
-
El art culo La ley
2019-04-29
El artículo “La ley del género” de Jacques Derrida es sumamente revelador en este punto, puesto que evidencia que en el concepto de género, que etimológicamente [genus] remite rivastigmine tartrate la proliferación, la generación, la creación, la hibridez y la mezcla, se halla implícita una orden o
-
br The Maputo Declaration on Strengthening of
2019-04-29

The 2008 Maputo Declaration on Strengthening of Laboratory Systems and the subsequent 2012 African Society for Laboratory Medicine Ministerial Call for Action drew attention to the importance of laboratory services. Most recently, laboratories have gained prominence in the accurate detection of in
-
Oe et al studied the prevalence
2019-04-29
Oe et al. studied the prevalence of BS in juveniles [14]. They reported that only one (0.005%) of 21,944 first-year elementary school children (6–7 years old) showed a type 1 ECG, and three showed type 2 or type 3 ECGs. Yamakawa et al. investigated the prevalence of Brugada-type ECG (types 1–3) in 2
-
br Conclusions br Conflict of interest br Introduction Brent
2019-04-29
Conclusions Conflict of interest Introduction Brentuximab vedotin (BV) is an anti-CD30 monoclonal antibody, cAC10(SGN-30), which combined with cytotoxic agent monomethyl auristatin E(MMAE) by a valine-citrulline peptide linker becomes a standard and effective therapy for patients with relap
-
Conduction delay is known to give rise to
2019-04-29
Conduction delay is known to give rise to notching of the QRS complex. When it occurs on the rising phase of the R wave, it is due to a conduction defect within the ventricle. When it occurs at the terminal portion of the QRS, thus masquerading as a J wave, it may be due to either a conduction defec
-
Para el a o Il ya ten a consolidada
2019-04-29
Para el año 2010, Ilê ya tenía consolidada una escuela popular en pleno barrio Liberdade, había influenciado en la emergencia de muchos otros afrobahianos, era considerado parte fundamental del patrimonio cultural de Salvador, y comienzaba order Pepstatin A permitir la participación de mestizos y b
-
Si bien en Argentina la democracia
2019-04-29
Si bien en Argentina la democracia se alcanzó por el colapso de la dictadura, la guerra de Malvinas, la misma estaba planifi en las “Bases para la Intervención de las Fuerzas Armadas en el Proceso Nacional”. En este documento se indicaba que el proceso se desarrollaría mediante la ejecución de tres
-
Findings Across Kenya Rwanda Tanzania and Uganda
2019-04-29
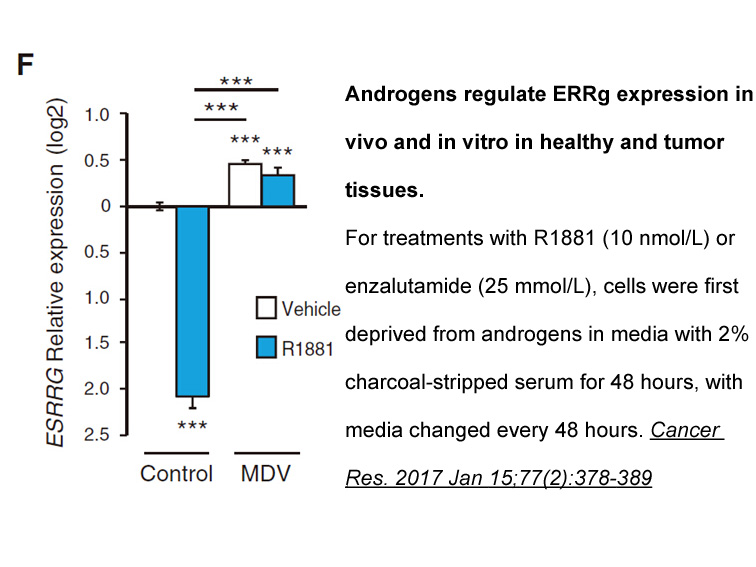
Findings Across Kenya, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda, for every 1°C degree of warming we predict that D609 mean calorie consumption would be reduced by 2·20% (95% CI 0·93–3·51); the percentage of undernourished children would increase by 2·40% (1·1–4·1); the incidence of moderate stunting would incr
-
br Acknowledgments This study was supported by
2019-04-29
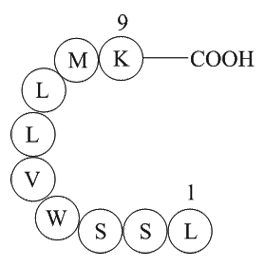
Acknowledgments This study was supported by a grant from the National Science Council (NSC 98-2314-B-075B-007-MY2). Introduction Many complications may occur following treatment of femoral shaft open fracture such as nonunion, malunion, delay union, bone defect, bone and joint deformity or st
-
In contrast the use of SF and MF
2019-04-28
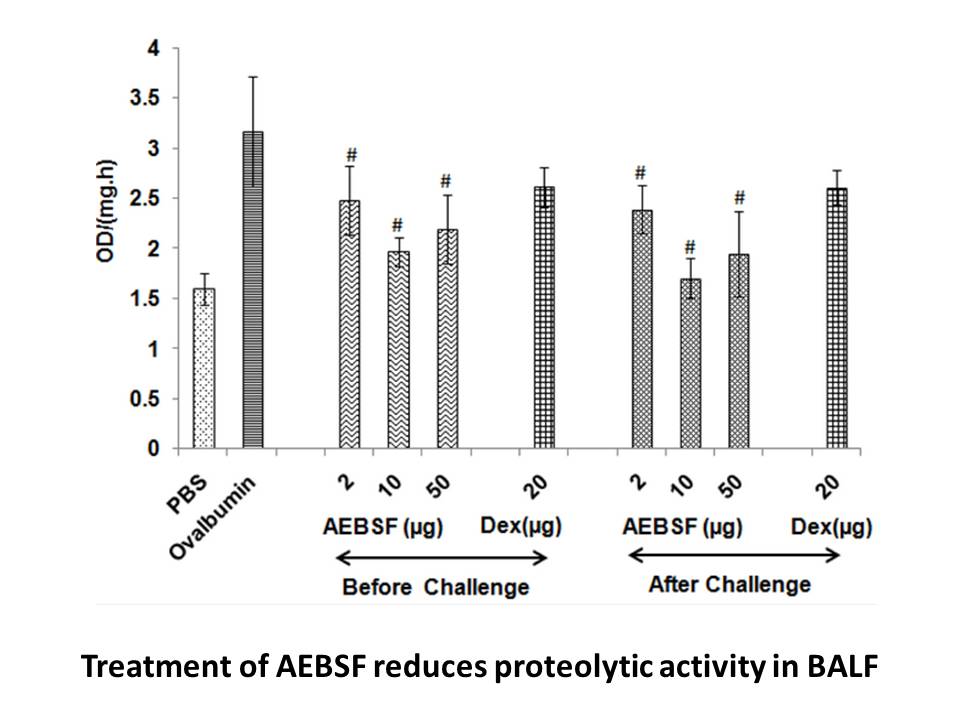
In contrast, the use of SF and MF radiation therapy treatments vary in patients with complicated bone metastases. A randomized controlled trial by Patchell et al. evaluating the efficacy of direct decompressive surgery showed that decompressive surgical resection and post-operative MF radiation ther
-
Con aquellos pa ses Argentina ha tenido
2019-04-28

Con aquellos países Argentina ha tenido una importante relación comercial. Contrariamente AMD3100 lo sucedido con Brasil, China y Estados Unidos, Argentina tuvo con cada uno de los cuatro países no potencias una balanza comercial superavitaria, en algunos casos de saldo positivo muy holgado. Hubo un
-
Colebunders and Felicity Fitzgerald and their
2019-04-28
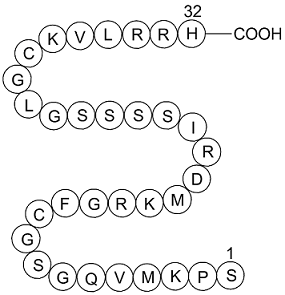
Colebunders and Felicity Fitzgerald and their colleagues also question whether we overestimate the potential for nosocomial Ebola virus transmission. In melanin with the low nosocomial transmission ates that they cite in Freetown, our experience in rural areas—which are so much more poorly resource
-
Dinoprostone has been administered either vaginally or intra
2019-04-28
Dinoprostone has been administered either vaginally or intracervically, rather successfully and without serious side effects in normal pregnancies. The most important adverse reaction of dinoprostone is uterine hyperstimulation. The incidence of uterine hyperstimulation ranged from 5% to 16% in pati
16607 records 1077/1108 page Previous Next First page 上5页 10761077107810791080 下5页 Last page